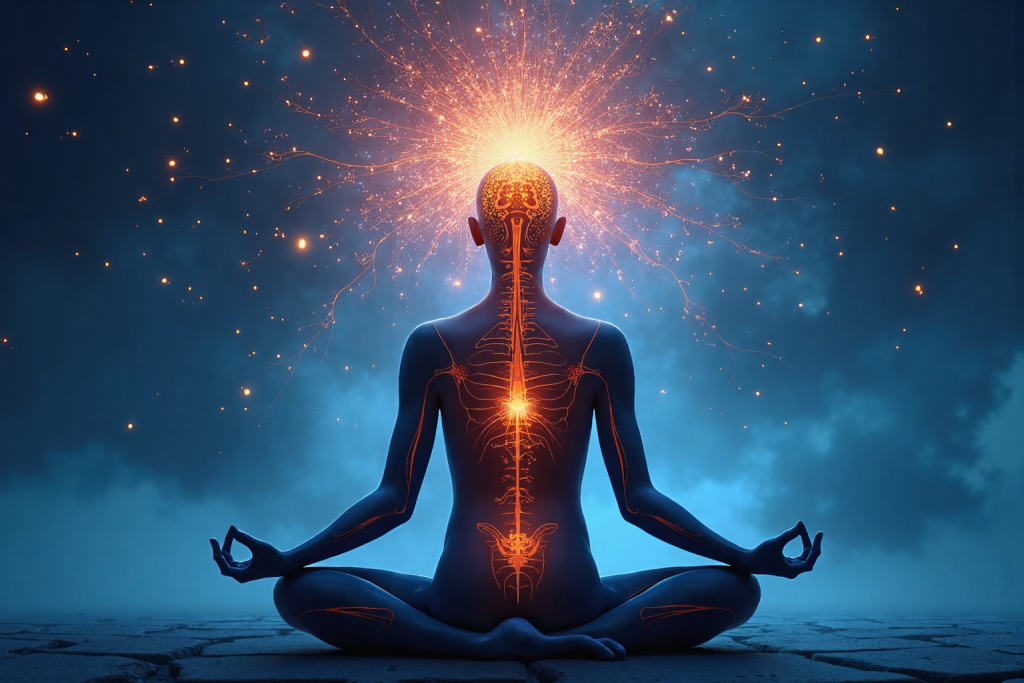
Introduction: Unlocking the Power of Neurological Relaxation
In today’s relentlessly demanding world, chronic stress has evolved from a fleeting inconvenience to a pervasive health crisis, insidiously eroding our physical and mental well-being. The constant barrage of stimuli and expectations triggers a cascade of physiological responses, keeping our nervous system in a perpetual state of hyperarousal. While readily accessible relaxation techniques like simple deep breathing exercises offer a modicum of relief, their impact often proves insufficient to counteract the deeply entrenched patterns of stress reactivity.
Exploring advanced neurological relaxation methods, grounded in the principles of neuroscience, offers the potential for deeper, more sustainable, and transformative benefits, moving beyond mere symptom management to address the root causes of stress. Neurological relaxation techniques represent a sophisticated approach to stress reduction, targeting the intricate interplay between the brain and body. These methods leverage the brain’s inherent plasticity, its capacity to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. By consciously engaging in practices such as mindfulness meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and autogenic training, we can actively reshape our neural pathways, fostering a greater sense of calm and resilience.
These techniques work by modulating brainwave frequencies, shifting from the high-frequency beta waves associated with alertness and anxiety to the slower alpha and theta waves characteristic of relaxation and focused attention. This shift promotes a state of mental quietude, allowing the nervous system to downregulate and restore its natural equilibrium. One of the key mechanisms underlying the effectiveness of neurological relaxation lies in its ability to stimulate the vagus nerve, the longest cranial nerve in the body and a crucial component of the parasympathetic nervous system, often referred to as the “rest and digest” system.
Vagus nerve stimulation triggers a cascade of beneficial effects, including a reduction in heart rate and blood pressure, a decrease in the production of stress hormones like cortisol, and an increase in the release of calming neurotransmitters such as GABA and serotonin. Furthermore, stimulating the vagus nerve has been shown to improve digestion, boost the immune system, and enhance overall mood and emotional regulation. Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing, humming, and cold water immersion are known to effectively activate the vagus nerve, promoting a state of deep relaxation and physiological balance.
This comprehensive guide delves into a range of these powerful techniques, meticulously exploring their scientific basis and providing practical, step-by-step instructions for seamlessly incorporating them into your daily life. We will examine practices such as Progressive Muscle Relaxation, a technique that systematically releases muscular tension to alleviate physical stress; Yoga Nidra, a guided meditation that induces a state of profound relaxation akin to sleep; Autogenic Training, which utilizes self-suggestion to promote calmness and physiological balance; and Biofeedback, a method that provides real-time feedback on physiological parameters to enhance self-awareness and control. By understanding the neuroscience behind these techniques and mastering their practical application, you can unlock your innate capacity for stress reduction, anxiety relief, sleep improvement, and enhanced overall well-being, paving the way for a healthier, more balanced, and fulfilling life.
The Neuroscience of Relaxation: How It Works
Neurological relaxation isn’t merely a feeling of calmness; it’s a measurable physiological shift that profoundly impacts the nervous system. It represents a state of deep rest characterized by reduced activity in the sympathetic nervous system (responsible for the “fight-or-flight” response) and increased activity in the parasympathetic nervous system (responsible for “rest-and-digest”). This shift is orchestrated by a complex interplay of brainwave activity, neurotransmitter release, and vagal nerve stimulation. These techniques effectively regulate brainwave activity, guiding the brain from the alert beta waves of waking consciousness toward the calmer alpha and theta waves associated with relaxation and deep meditation.
This transition allows the mind to settle, reducing mental chatter and promoting a sense of tranquility. For instance, studies using EEG have shown a significant increase in alpha wave activity during practices like mindfulness meditation and yoga nidra, indicating a shift towards a relaxed state. Dr. Andrew Weil, a renowned expert in integrative medicine, emphasizes the importance of actively engaging the parasympathetic nervous system through relaxation techniques to counteract the detrimental effects of chronic stress.
He notes that consistent practice can lead to long-term improvements in stress resilience and overall well-being. These techniques promote the release of calming neurotransmitters such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and serotonin. GABA acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, reducing neuronal excitability and promoting feelings of calm and relaxation. Serotonin plays a crucial role in mood regulation, sleep, and appetite, contributing to a sense of overall well-being. Studies have demonstrated that relaxation techniques like meditation can increase serotonin levels, which may explain their effectiveness in managing anxiety and depression.
For example, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that mindfulness-based stress reduction significantly reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression in participants, correlating with increased serotonin levels. This neurochemical shift is a key component of the deep relaxation achieved through these practices. Furthermore, neurological relaxation techniques stimulate the vagus nerve, a major component of the parasympathetic nervous system. The vagus nerve acts as a communication pathway between the brain and many organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive system.
Stimulating the vagus nerve through practices like deep breathing and chanting can slow heart rate, lower blood pressure, and promote digestive health. This vagal activation is central to the relaxation response, a physiological state of deep rest that counteracts the stress response. The vagus nerve acts as a brake pedal for the nervous system, helping to regulate the body’s response to stress and promoting a state of equilibrium. Research shows that individuals with higher vagal tone (a measure of vagus nerve activity) tend to have better emotional regulation, resilience to stress, and overall physical health. By incorporating practices that stimulate the vagus nerve, individuals can actively cultivate a more balanced and resilient nervous system, leading to improved stress management and enhanced well-being. This intricate interplay of brainwave activity, neurotransmitter release, and vagal nerve stimulation underscores the powerful impact of neurological relaxation techniques on both mental and physical health.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR) offers a systematic approach to stress reduction by targeting the intricate connection between the mind and body. This technique involves consciously tensing and releasing different muscle groups, promoting deep relaxation and a sense of calm. The process begins by focusing on a specific muscle group, such as the toes, tensing them for a few seconds, and then releasing the tension while noticing the sensation of relaxation. This process is repeated sequentially, working through various muscle groups in the body, from the feet to the face.
The beauty of PMR lies in its simplicity and accessibility, requiring no special equipment or prior experience. By actively engaging with the physical sensations of tension and release, individuals can cultivate a heightened awareness of their body’s stress responses and develop the ability to consciously regulate them. PMR’s effectiveness stems from its impact on the nervous system. By consciously inducing and releasing muscle tension, PMR helps to break the cycle of chronic stress, which often manifests as persistent muscle tension.
This technique promotes the release of calming neurotransmitters, such as GABA and serotonin, which counter the effects of stress hormones like cortisol. Additionally, PMR can stimulate the vagus nerve, a key component of the parasympathetic nervous system responsible for the relaxation response. This vagal activation helps to slow heart rate, lower blood pressure, and promote a sense of tranquility. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Behavioral Medicine found that PMR significantly reduced anxiety levels in participants compared to a control group.
The practice of PMR can be readily integrated into daily life, offering a powerful tool for managing stress in various situations. Whether practiced before bedtime to promote restful sleep, during a stressful workday to alleviate tension, or before a high-pressure presentation to enhance focus, PMR provides tangible benefits. A 2019 study in the journal “Stress and Health” demonstrated that regular PMR practice improved sleep quality in individuals with insomnia. Moreover, PMR can be combined with other relaxation techniques, such as yoga nidra or autogenic training, to create a synergistic effect and amplify the benefits of each method.
Developing a personalized relaxation routine that incorporates PMR can empower individuals to effectively manage stress, improve overall well-being, and cultivate a greater sense of self-awareness. To maximize the benefits of PMR, it is essential to create a conducive environment for practice. Find a quiet space where you can lie down or sit comfortably without distractions. Close your eyes and focus on your breath, allowing it to deepen and slow down. As you tense each muscle group, pay close attention to the sensations of tension, and as you release, notice the contrasting feeling of relaxation.
Starting with shorter sessions of 5-10 minutes and gradually increasing the duration as you become more comfortable can enhance the effectiveness of the practice. Guided PMR audios can also provide helpful support, especially for beginners. If you experience any challenges or discomfort, consulting with a qualified relaxation therapist or healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and support. Incorporating PMR into your daily routine can be transformative, empowering you to take control of your stress response and cultivate a deeper sense of calm and well-being. As with any new skill, consistency is key. Regular practice will not only enhance your ability to relax but also build resilience to stress over time, ultimately contributing to a healthier and more balanced life.
Yoga Nidra: Achieving Deep Relaxation Through Guided Meditation
“Yoga Nidra: Achieving Deep Relaxation Through Guided Meditation”\n\nYoga Nidra, often referred to as “yogic sleep,” is a powerful guided meditation technique that facilitates a state of profound relaxation while maintaining conscious awareness. Unlike traditional sleep, Yoga Nidra cultivates a state of dynamic stillness where the body rests deeply, and the mind remains alert yet tranquil. This practice systematically guides practitioners through various stages, including rotation of consciousness (bringing awareness to different body parts), breath awareness, and visualization, to access a state of deep relaxation and promote physical and mental restoration.\n\nThe practice typically begins by finding a comfortable lying down position, similar to Savasana in traditional Hatha yoga.
A facilitator then guides the practitioner through a series of verbal instructions. These instructions often begin with setting a Sankalpa, or a positive intention for the practice. As the practice unfolds, the instructions direct attention to different parts of the body, promoting a deep sense of relaxation and body awareness. This systematic rotation of consciousness helps to release muscular tension and calm the nervous system. Further instructions may incorporate breath awareness, encouraging practitioners to observe the natural rhythm of their breath without manipulation, further deepening the relaxation response.
Visualizations and guided imagery may also be incorporated to further quiet the mind and enhance the experience of deep rest.\n\nFrom a neuroscientific perspective, Yoga Nidra has been shown to induce a shift in brainwave activity, promoting a predominance of alpha and theta waves, which are associated with relaxation, creativity, and deep meditative states. This shift in brainwave activity can lead to a decrease in stress hormones like cortisol and an increase in neurotransmitters like GABA and serotonin, which promote feelings of calm and well-being.
Moreover, Yoga Nidra has been found to stimulate the vagus nerve, a key component of the parasympathetic nervous system responsible for the “rest and digest” response. This vagal stimulation further enhances the relaxation response and contributes to a cascade of physiological benefits, including reduced heart rate, lower blood pressure, and improved digestion.\n\nYoga Nidra offers a range of benefits for stress reduction, anxiety relief, and sleep improvement. By calming the nervous system and promoting deep relaxation, it can help to alleviate the symptoms of chronic stress and improve overall resilience.
For individuals struggling with anxiety, Yoga Nidra can provide a powerful tool for managing anxious thoughts and promoting a sense of inner peace. Furthermore, the practice has been shown to improve sleep quality by reducing sleep latency and increasing the duration of deep sleep. A study published in the “Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine” found that regular practice of Yoga Nidra significantly improved sleep quality in individuals with insomnia.\n\nIncorporating Yoga Nidra into a regular routine can be easily achieved with readily available guided meditations online or through in-person classes.
Beginners are encouraged to start with shorter practices of 10-15 minutes and gradually increase the duration as they become more comfortable. Consistency is key to experiencing the full benefits of Yoga Nidra, and even short, regular practices can have a profound impact on overall well-being. It is an accessible and effective technique for anyone seeking to cultivate deep relaxation, manage stress, and enhance their overall health and well-being. When combined with other relaxation techniques like Progressive Muscle Relaxation or Autogenic Training, the benefits can be further amplified, creating a synergistic approach to stress management and relaxation.
Autogenic Training: Harnessing the Power of Self-Suggestion
Autogenic Training (AT) is a powerful self-regulation technique that leverages the mind-body connection to achieve deep relaxation and manage stress. It operates on the principle of self-suggestion, using specific phrases to evoke physiological and psychological responses associated with calmness. By repeating phrases like “My arms are heavy and warm,” or “My heartbeat is calm and regular,” practitioners can influence their autonomic nervous system, promoting a shift from the sympathetic (fight-or-flight) to the parasympathetic (rest-and-digest) state.
This shift is crucial for stress reduction, anxiety relief, and overall well-being. AT provides a readily accessible tool to actively engage with the nervous system and promote relaxation, unlike passive relaxation techniques. Its efficacy stems from the brain’s remarkable capacity for neuroplasticity, where repeated mental activity can induce tangible physiological changes. Research suggests that consistent practice of AT can lead to decreased heart rate, lowered blood pressure, and reduced muscle tension, demonstrating its potential as a valuable tool for stress management and improving various health markers.
The practice of Autogenic Training typically involves six standard exercises, each focusing on a different physiological sensation: heaviness in the limbs, warmth in the limbs, regulation of cardiac activity, regulation of breathing, abdominal warmth, and coolness of the forehead. These exercises are progressively mastered, beginning with the sensation of heaviness, then warmth, and so on. The repetitive nature of the phrases, combined with focused attention, helps to quiet the mind and induce a state of deep relaxation similar to that achieved through meditation or yoga nidra.
The benefits extend beyond mere physical relaxation; AT has also been shown to improve sleep quality, reduce chronic pain, and enhance emotional regulation. By influencing the vagus nerve, a key component of the parasympathetic nervous system, AT promotes the release of calming neurotransmitters like acetylcholine and GABA, further contributing to the overall sense of tranquility and well-being. This vagal nerve stimulation is a cornerstone of many relaxation techniques and is a key mechanism through which AT exerts its beneficial effects.
While the phrases themselves may seem simple, the power of AT lies in the consistent and focused practice. Like any skill, mastering autogenic training requires patience and dedication. Beginners may find it helpful to practice in a quiet, comfortable environment free from distractions. Guided audio recordings can be particularly useful, especially in the initial stages, to ensure proper technique and maintain focus. As proficiency develops, individuals can adapt the practice to suit their specific needs and preferences, incorporating the techniques into their daily routine to manage stress, improve sleep, or enhance overall well-being. Integrating AT with other relaxation methods like progressive muscle relaxation or mindfulness meditation can create a synergistic effect, further amplifying the benefits and providing a comprehensive approach to stress reduction and improved neurological function. Furthermore, consulting with a qualified therapist or instructor can provide personalized guidance and address any challenges encountered during the learning process, ensuring a safe and effective practice.
Biofeedback: Real-Time Monitoring for Enhanced Relaxation
Biofeedback: Harnessing Technology for Precision Relaxation Biofeedback represents a cutting-edge approach to relaxation, employing electronic devices to monitor physiological functions such as heart rate, muscle tension, skin temperature, and brainwave activity. This real-time feedback empowers individuals to gain a deeper understanding of their body’s responses to stress and learn to consciously control them, promoting relaxation and reducing stress. By providing tangible data, biofeedback bridges the gap between the mind and body, fostering a greater sense of self-awareness and control over physiological processes.
One of the key mechanisms through which biofeedback promotes relaxation is by regulating the autonomic nervous system (ANS). The ANS governs involuntary bodily functions, including heart rate, respiration, and digestion. Stress typically activates the sympathetic branch of the ANS, leading to the “fight-or-flight” response. Biofeedback helps individuals activate the parasympathetic branch, responsible for the “rest-and-digest” response, thus promoting a state of calm. For example, heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback trains individuals to increase the variation in time intervals between heartbeats, a key indicator of healthy vagal tone and resilience to stress.
Research suggests that improved HRV is linked to reduced anxiety, improved sleep, and enhanced emotional regulation. Different types of biofeedback modalities cater to specific needs. Electromyography (EMG) biofeedback measures muscle tension, helping individuals identify and release muscular holding patterns that contribute to stress and pain. Temperature biofeedback provides insights into peripheral blood flow, which is influenced by stress levels. By learning to increase peripheral temperature, individuals can promote relaxation and reduce anxiety. Neurofeedback, a specialized form of biofeedback, focuses on brainwave activity.
By training individuals to shift their brainwave patterns towards more relaxed states, neurofeedback can address issues such as anxiety, insomnia, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The benefits of biofeedback extend beyond immediate relaxation. Regular practice cultivates self-regulation skills that empower individuals to manage stress more effectively in daily life. By becoming attuned to their body’s signals and developing strategies to modulate physiological responses, individuals can interrupt the stress cycle before it escalates. This enhanced self-awareness translates into improved coping mechanisms, reduced reactivity to stressors, and greater emotional resilience.
Moreover, biofeedback can complement other relaxation techniques like progressive muscle relaxation and yoga nidra, amplifying their effects and promoting deeper states of relaxation. While biofeedback offers significant advantages, it’s essential to approach it with realistic expectations. It’s not a quick fix but rather a skill that develops over time with consistent practice. Working with a qualified biofeedback therapist is crucial, especially initially, to ensure proper technique and personalized guidance. The therapist can help determine the most appropriate biofeedback modality for individual needs, interpret the feedback data, and develop a tailored training program. As individuals gain proficiency, they can continue practicing independently, integrating biofeedback into their daily routine to maintain and enhance their relaxation skills.
Combining Techniques for Optimal Results: Creating a Personalized Relaxation Routine
Synergistic Relaxation: Combining Techniques for Optimal Results\n\nWhile individual relaxation techniques like Progressive Muscle Relaxation, Yoga Nidra, Autogenic Training, and Biofeedback offer significant benefits, combining these methods can create a synergistic effect, amplifying stress reduction and enhancing overall well-being. This personalized approach allows you to tailor your relaxation routine to your specific needs and preferences, maximizing the impact on your neurological system.\n\nIntegrating Progressive Muscle Relaxation with Yoga Nidra, for instance, can deepen the relaxation experience. By first releasing physical tension through progressive muscle relaxation, you prepare your body and mind for the deeper meditative state of Yoga Nidra.
This combination promotes both physical and mental relaxation, effectively reducing stress and improving sleep quality. Research suggests that the conscious awareness cultivated in Yoga Nidra can enhance the body’s ability to release muscle tension, further amplifying the benefits of progressive relaxation.\n\nCombining Autogenic Training with Biofeedback offers another powerful synergistic approach. Autogenic training utilizes self-suggestions to influence physiological states, while biofeedback provides real-time feedback on these changes. This combination allows you to consciously regulate bodily functions like heart rate and muscle tension, promoting a deeper understanding of your body’s stress response and enhancing your ability to control it.
Studies have shown that this combined approach can be particularly effective in managing anxiety and promoting relaxation.\n\nCreating a personalized relaxation routine involves experimenting with different combinations and observing their effects on your body and mind. You might find that practicing Progressive Muscle Relaxation before bedtime, followed by a short Yoga Nidra session, promotes restful sleep. Alternatively, combining Autogenic Training with Biofeedback during stressful situations can enhance your coping mechanisms and reduce anxiety. By exploring these synergistic combinations, you can discover the most effective approach for achieving optimal relaxation and well-being.\n\nMindfulness meditation can be integrated with any of these techniques to enhance self-awareness and deepen the relaxation response.
Adding a mindfulness component encourages focused attention on the present moment, reducing rumination and promoting a sense of calm. The vagus nerve, a key component of the parasympathetic nervous system, is stimulated through these practices, leading to a cascade of physiological changes that promote relaxation and reduce stress. By incorporating mindfulness into your routine, you cultivate a greater awareness of your body’s signals, allowing you to identify and address stress triggers more effectively.\n\nBuilding a personalized relaxation routine requires patience and self-exploration.
Start by incorporating one or two techniques into your daily schedule and gradually experiment with different combinations. Pay attention to how your body and mind respond to each practice and adjust your routine accordingly. Consulting with a qualified health professional or relaxation therapist can provide further guidance and support in developing a tailored program that meets your individual needs and goals. Ultimately, a synergistic approach to relaxation empowers you to take control of your well-being and cultivate a deeper sense of calm and resilience in the face of life’s challenges.
Practical Applications: Integrating Relaxation into Daily Life
Integrating neurological relaxation techniques into your daily routine can significantly enhance your overall well-being. These practices offer accessible and effective tools for managing stress, improving sleep quality, and promoting a greater sense of calm. By weaving these techniques into the fabric of your day, you empower yourself to navigate challenges with resilience and cultivate a more balanced lifestyle. To improve sleep quality, consider practicing progressive muscle relaxation or yoga nidra before bedtime. These techniques calm the nervous system and prepare the body for restful sleep.
Studies have shown that regular practice of relaxation techniques can lead to significant improvements in sleep duration and quality, reducing symptoms of insomnia and promoting deeper, more restorative sleep. By incorporating these practices into your nightly routine, you can create a conducive environment for optimal sleep hygiene and wake up feeling refreshed and revitalized. During stressful situations, implementing techniques like autogenic training or mindful breathing can provide immediate relief. Autogenic training, with its focus on self-suggestions and visualizations, can help regulate physiological responses to stress, such as heart rate and muscle tension.
Mindful breathing, a cornerstone of many relaxation practices, activates the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting a sense of calm and reducing anxiety. These readily available tools empower you to manage stress effectively in the moment, fostering emotional regulation and enhancing coping mechanisms. To improve focus and concentration before important tasks, consider incorporating short sessions of biofeedback or meditation. Biofeedback provides real-time feedback on physiological responses, allowing you to develop greater awareness and control over your body’s reactions to stress.
This enhanced awareness can translate into improved focus and concentration. Meditation, through its focus on present moment awareness, can quiet the mental chatter that often interferes with concentration. Research suggests that regular meditation practice can enhance attention span and cognitive function, leading to improved performance and productivity. Furthermore, integrating these techniques into daily life can have a cumulative effect on overall well-being. Regular practice of neurological relaxation techniques can lead to a decrease in stress hormones like cortisol, promoting a more balanced hormonal profile.
This, in turn, can positively impact various aspects of health, including cardiovascular health, immune function, and digestive health. By making these practices a consistent part of your life, you cultivate a proactive approach to stress management and create a foundation for long-term health and well-being. Finally, consider creating a personalized relaxation routine that combines different techniques to maximize their benefits. Experiment with incorporating progressive muscle relaxation, yoga nidra, autogenic training, biofeedback, and mindfulness into your daily schedule. Listen to your body’s cues and adjust your routine as needed. By tailoring your approach to relaxation, you can create a sustainable practice that effectively addresses your individual needs and supports your journey towards enhanced well-being.
Potential Challenges and Solutions: Troubleshooting Tips for Effective Relaxation
Even with the most promising relaxation techniques, some individuals may initially encounter difficulties. This is perfectly normal. The key is patience and persistence. Begin with shorter practice sessions, perhaps just 5-10 minutes, and gradually increase the duration as you become more comfortable and proficient. For example, if you’re struggling with progressive muscle relaxation, start by focusing on just one or two muscle groups before expanding to a full-body routine. Similarly, with Yoga Nidra, you might initially find it challenging to maintain awareness without drifting off to sleep; shorter sessions and a focus on the breath can help build your concentration.
Remember, neurological relaxation is a skill that improves with practice. One common challenge is mental restlessness. Many people find it difficult to quiet their minds and focus on the present moment, a crucial element for effective stress reduction. If you experience racing thoughts during meditation or autogenic training, acknowledge them without judgment and gently redirect your attention back to your breath, the guided instructions, or the self-suggestion. Techniques like mindfulness meditation, which specifically trains attention and awareness, can be particularly helpful in overcoming this obstacle.
Research has shown that regular mindfulness practice can alter brainwave activity, promoting a more relaxed and focused state, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness of other relaxation techniques. Another potential hurdle is physical discomfort. Finding a comfortable position is essential for deep relaxation. Experiment with different postures and supports, such as pillows or blankets, to alleviate any strain or tension. For individuals with chronic pain or physical limitations, modified versions of techniques like progressive muscle relaxation and yoga nidra may be necessary.
Consulting with a physical therapist or yoga instructor experienced in adaptive techniques can provide valuable guidance. Biofeedback can also be a useful tool in identifying and addressing specific areas of muscle tension contributing to discomfort, allowing for targeted relaxation interventions. Furthermore, it’s important to consider the environment in which you practice. A noisy or distracting environment can significantly impede your ability to relax. Create a calm and quiet space where you can minimize interruptions. This might involve dimming the lights, using earplugs or noise-canceling headphones, or playing soothing music.
Consistency is also key. Establishing a regular relaxation routine, even if it’s just for a few minutes each day, can help train your nervous system to respond more readily to relaxation techniques. Finally, if you consistently encounter significant challenges or experience increased anxiety or distress, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified instructor, therapist, or healthcare professional. They can provide personalized guidance, address underlying issues, and ensure that the techniques are appropriate for your individual needs. A therapist specializing in stress management or anxiety relief may also introduce complementary approaches, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), to further enhance your overall well-being and ability to achieve neurological relaxation and vagus nerve stimulation.
Conclusion: Embrace Relaxation for a Healthier, More Balanced Life
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of advanced neurological relaxation techniques in reducing stress, anxiety, and improving sleep quality. Research consistently shows that practices like progressive muscle relaxation, yoga nidra, autogenic training, and biofeedback can positively impact brainwave activity, shifting from the active beta waves to the calmer alpha and theta states. This shift in brainwave activity is associated with a decrease in the stress hormones cortisol and adrenaline, promoting a sense of tranquility and well-being.
Furthermore, these techniques influence neurotransmitter levels, increasing the production of GABA, a neurotransmitter known for its calming effects, and serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in mood regulation and sleep. Improved vagal tone, a measure of the activity of the vagus nerve, is another crucial benefit, as the vagus nerve plays a vital role in the parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for the body’s relaxation response. Stimulating the vagus nerve through these relaxation techniques helps to counter the effects of chronic stress and promotes a state of calm.
The impact of these techniques extends beyond mere relaxation. Dr. Herbert Benson, a pioneer in mind-body medicine, found that eliciting the relaxation response through practices like meditation can lead to significant physiological changes, including decreased blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen consumption. These changes contribute to improved cardiovascular health and overall resilience to stress. For instance, a study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that mindfulness-based stress reduction, which incorporates several neurological relaxation techniques, was effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Real-world examples abound, with individuals reporting improved sleep, better focus, and enhanced emotional regulation after incorporating these practices into their daily routines. One individual, a high-powered executive struggling with chronic stress and insomnia, found that regular practice of yoga nidra significantly improved her sleep quality and reduced her anxiety levels, allowing her to perform more effectively at work and enjoy a more balanced personal life. By incorporating these advanced neurological relaxation techniques into your life, you can cultivate a deeper sense of calm, resilience, and well-being.
Start by exploring different techniques and finding what resonates with you. Perhaps progressive muscle relaxation helps you release physical tension, while yoga nidra guides you to a state of deep mental relaxation. Experiment with different combinations and create a personalized relaxation routine that fits your lifestyle and addresses your specific needs. Consistency is key, as the benefits of these practices are cumulative. Even a few minutes of daily practice can make a noticeable difference in your stress levels, sleep quality, and overall sense of well-being. As you become more proficient, you can integrate these techniques into various aspects of your life, using them to manage stress during challenging situations, enhance focus before important tasks, or promote restful sleep at the end of the day. Embracing these practices empowers you to take control of your nervous system and cultivate a more balanced and fulfilling life.